Retinoids
The term retinoids refers to an entire family of ingredients. This is extremely large and includes not only retinal, retinol and retinoic acid, but also several other substances. All these forms are derivatives of vitamin A, which are summarised under the generic term retinoids. They are found in many cosmetic products and are converted into retinoic acid by our skin. Depending on the derivative, one to three steps are required for this conversion.
Retinoic acid itself is an active ingredient that requires a prescription because it often causes skin irritation. It may therefore only be used according to a doctor’s prescription, and the instructions for use recommended by the doctor must be strictly observed. For this reason, the milder esters of retinoic acid are used in cosmetics. They support collagen formation and thus give the skin more elasticity, vitality, and resilience. At the same time, they also inhibit the breakdown of collagen and help the skin to store more moisture. As a result, wrinkles are hardly visible. Retinoids also stimulate the formation of new horny cells, which refines the complexion and makes it look more even.
Retinoids also have an antioxidant effect, which means they are able to eliminate free radicals. This prevents the skin from ageing prematurely due to various influences. Also interesting for cosmetic use: Retinoids have the ability to lighten the skin, which they achieve by inhibiting tyrosinase activity. Thus, disturbing pigment spots, skin discolourations and freckles become almost invisible.
We present the most important retinoids below.
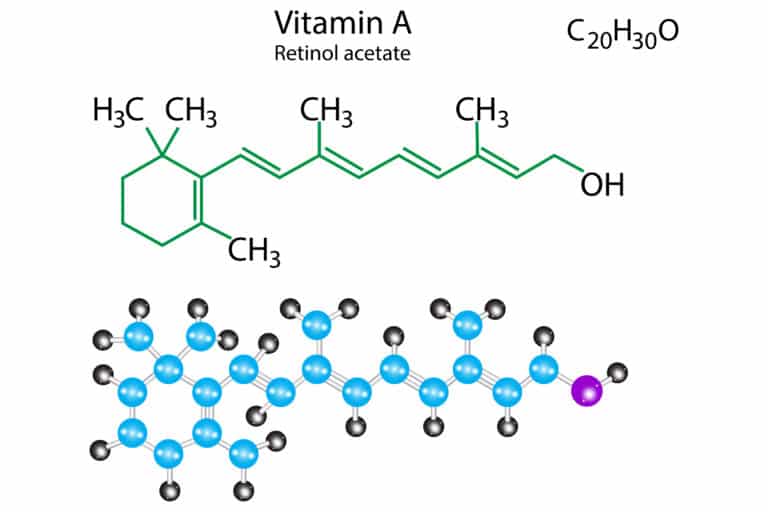
Overview of retinoids: Retinyl acetate
Retinyl acetate, like many other derivatives of vitamin A, is often used in skin care creams, sunscreens, and lotions. As an ester between acetic acid and retinol, it is mainly known for its very good anti-ageing effect.
It is also found in products such as toothpaste and cough drops. Furthermore, retinyl acetate is an officially authorised feed additive (according to Regulation (EC) No 1831/2003).
Fact Sheet Retinyl Acetate
INCI: Retinyl Acetate
CAS number: 127-47-9
Description: yellow, crystalline
Overview Retinoids: Retinyl Retinoate
Retinyl retinoate is considered the royal class among the vitamin A derivatives. It can provide clearly visible results after only four weeks, i.e., wrinkles and lines are significantly reduced. Pigmentation is also reduced. Retinyl retinoate is said to be up to eight times more effective than retinol. It can be combined particularly well with vitamin E, vitamin C and hyaluronic acid. This way, the best possible effect can be achieved. In addition, retinyl retinoate is even said to be able to stimulate the production of the body’s own hyaluronic acid.
Fact Sheet Retinyl Retinoate
INCI: Retinyl Retinoate
CAS number: 15498-86-9
Description: an innovative and still relatively new active ingredient that is formed by the binding of retinol to retinoic acid.
Effect: increases collagen synthesis, smoothes the skin, ensures an even skin tone
Overview Retinoids: Hydroxypinacolone Retinoate
Hydroxypinacolone retinoate has very good anti-ageing properties and can regulate the metabolism of the skin epidermis and stratum corneum. It brightens the skin, prevents premature ageing, improves the skin structure and can even help against acne. It is also considered very stable and particularly well tolerated.
Fact Sheet Hydroxypinacolone Retinoate
INCI: Hydroxypinacolone Retinoate
CAS number: 893412-73-2
Description: yellow powder
Overview Retinoids: Retinyl palmitate
Retinyl palmitate is the carboxylic acid ester and results from the esterification of retinol and palmitic acid. The active ingredient is a typical and common ingredient in skin care products.
Fact Sheet Retinyl Palmitate
INCI: Retinyl Palmitate
CAS number: 79-81-2
EC number: 201-228-5
Description: viscous, partly yellow crystalline
Natural occurrence: in the liver of mammals, in fatty marine fish (e.g. halibut and cod), in butter, egg yolk and milk
Overview of retinoids: Retinol
Retinol is an essential and fat-soluble vitamin, also known as vitamin A1. It is often equated with vitamin A, but this is not quite correct, because strictly speaking, vitamin A is a whole group of substances. Retinol is a component of the visual pigment; a deficiency can lead to night blindness, for example. In cosmetic products, retinol can improve the skin’s ability to regenerate. It also ensures that the skin’s moisture balance remains in equilibrium. At the same time, retinol is an antioxidant that prevents the negative effects of free radicals. The use of products containing retinol often leads to a smooth and rosy complexion and can also be helpful in cases of acne.
Fact Sheet Retinol
INCI: Retinol
CAS number: 68-26-8
Description: yellow solid
Natural occurrence: Milk, egg yolk, liver, fish
Overview Retinoids: Retinal
Retinal is the aldehyde of retinol. It is considered particularly effective because it is the precursor of retinoic acid. Thus, only one step is required for the conversion. Studies have even shown that retinal is more effective overall than retinol.
Fact Sheet Retinal
INCI: Retinal
CAS numbers: 311338-94-0 (non-specific)
116-31-4 (all-trans)
564-87-4 (11-cis)
Overview Retinoids: Retinyl linoleate
Retinyl linoleate is a fatty acid ester formed from linoleic acid and all-trans-retinol.
Fact Sheet Retinyl Linoleate
INCI: Retinyl linoleate
CAS number: 631-89-0
Molecular formula: C38H60O2
Overview Retinoids: Retinyl Propionate
Retinyl propionate is a lesser-known member of the retinoid family. In this ester, retinol and propionic acid are bound together. Retinyl propionate is characterised by a unique metabolic profile and, in comparison to retinol and retinyl palmitate, convinces with a higher retinoid-related bioactivity.
Fact Sheet Retinyl Propionate
INCI: Retinyl Propionate
CAS number: 7069-42-3
Overview Retinoids: Retinyl Sunflowerseedate
Retinyl Sunflowerseedate is a bio-based, form-stable and non-irritating anti-ageing ingredient consisting of retinol and sunflower fatty acids.
INCI: Retinyl Sunflowerseedate
Retinoids as active ingredients for sophisticated cosmetic formulations
The large family of retinoids is mainly used in high-quality anti-ageing products because the active ingredients promote collagen synthesis, fight free radicals as antioxidants and improve the skin’s appearance. They are also able to lighten the skin, which is a great advantage especially in the case of pigment spots and other skin discolourations. Some active ingredients from the retinoid family can also be used as supportive therapy for acne. Are you interested in innovative formulations in which the derivatives of vitamin A are used? Ask us!
Literature
- Reversal of skin aging with topical retinoids; Bradley A Hubbard 1 , Jacob G Unger, Rod J Rohrich; Reconstr Surg 2014 Apr;133(4):481e-490e
- Tretinoin peel: a critical view.; Sumita JM, Leonardi GR, Bagatin E; Bras Dermatol. 2017 May-Jun;92(3):363-366
- Isotretinoin and Timing of Procedural Interventions: A Systematic Review With Consensus Recommendations.; Spring LK, Krakowski AC, Alam M, Bhatia A, Brauer J, Cohen J, Del Rosso JQ, Diaz L, Dover J, Eichenfield LF, Gurtner GC, Hanke CW, Jahnke MN, Kelly KM, Khetarpal S, Kinney MA, Levy ML, Leyden J, Longaker MT, Munavalli GS, Ozog DM, Prather H, Shumaker PR, Tanzi E, Torres A, Velez MW, Waldman AB, Yan AC, Zaenglein AL.; JAMA Dermatol. 2017 Aug 1;153(8):802-809
- Topical Over-the-Counter Antiaging Agents: An Update and Systematic Review.; Imhof L, Leuthard D.; Dermatology. 2021;237(2):217-229
- Skin aging: Pathophysiology and innovative therapies; Boismal F, Serror K, Dobos G, Zuelgaray E, Bensussan A, Michel L.; Med Sci (Paris). 2020 Dec;36(12):1163-1172
- A randomized, double-blind, controlled comparative trial of the anti-aging properties of non-prescription tri-retinol 1.1% vs. prescription tretinoin 0.025; Elizabeth T Ho , Nathan S Trookman, Brian R Sperber, Ronald L Rizer, Ralph Spindler, Sujatha Sonti, Vincent Gotz, Rahul Mehta; J Drugs Dermatol 2012 Jan;11(1):64-9
- Theoretical Study of the Photoisomerization Mechanism of All-Trans-Retinyl Acetate.; Kochman MA, Palczewski K, Kubas A.; J Phys Chem A. 2021 Sep 30;125(38):8358-8372
- Design and Engineering of „Green“ Nanoemulsions for Enhanced Topical Delivery of Bakuchiol Achieved in a Sustainable Manner: A Novel Eco-Friendly Approach to Bioretinol.; Lewińska A, Domżał-Kędzia M, Maciejczyk E, Łukaszewicz M, Bazylińska U.; Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 18;22(18):10091
- Effects of Topical Retinoids on Acne and Post-inflammatory Hyperpigmentation in Patients with Skin of Color: A Clinical Review and Implications for Practice. Callender VD, Baldwin H, Cook-Bolden FE, Alexis AF, Stein Gold L, Guenin E.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2022 Jan;23(1):69-81
- Arnhold: Der Begriff „Retinoide“ In: Untersuchungen zum Metabolismus von Vitamin A / Retinoiden im Hinblick auf eine Risikoabschätzung ihrer teratogenen Wirkung beim Menschen; S.2; Dissertation; Braunschweig, 07.03.2000
- Anti-Irritant Strategy against Retinol Based on the Genetic Analysis of Korean Population: A Genetically Guided Top-Down Approach.; Kang S, Kim K, Jun SH, Lee S, Kim J, Shin JG, Kim Y, Kim M, Park SG, Kang NG.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Nov 25;13(12):2006