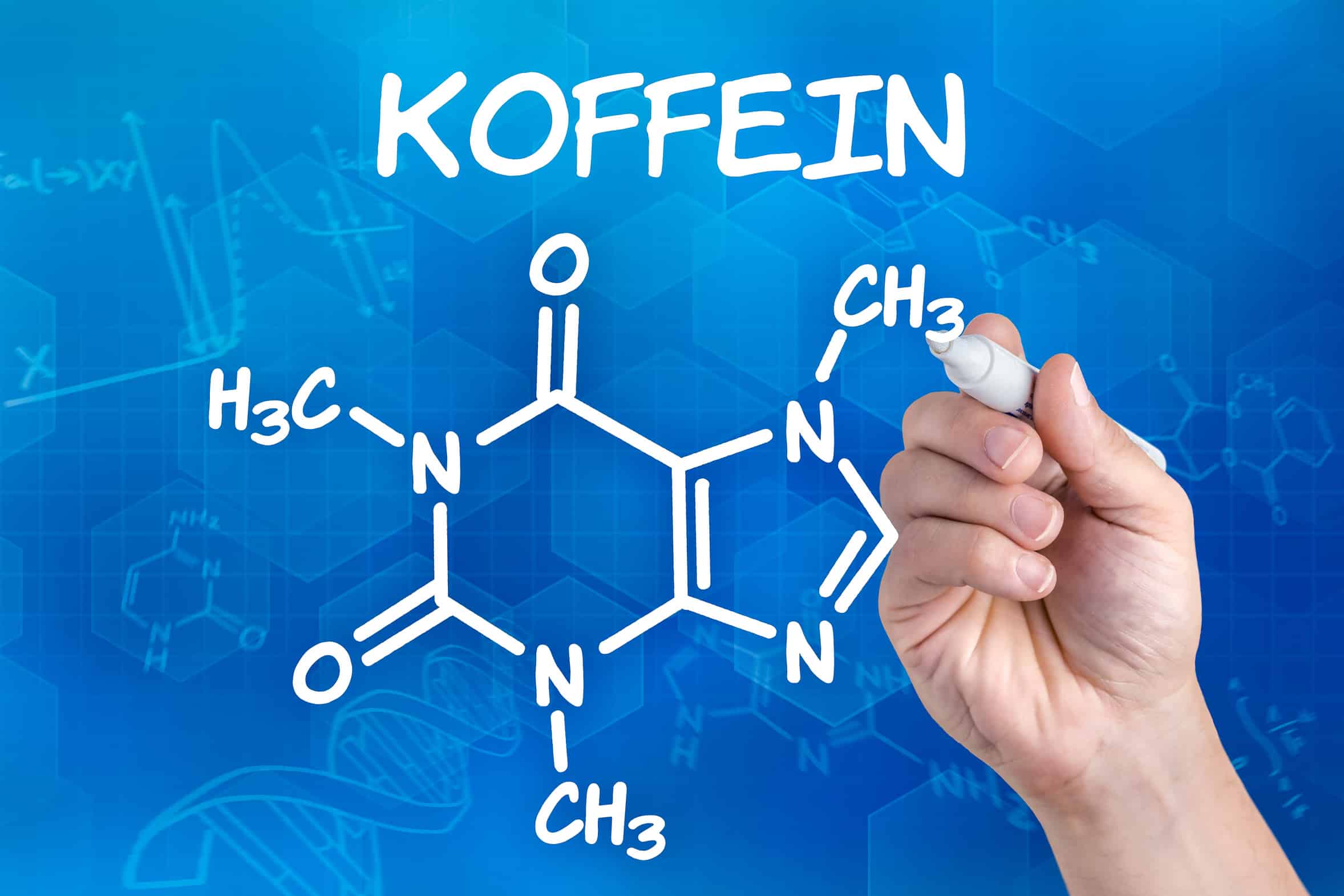
Caffeine
Effect of caffeine
Caffeine has a wide range of pharmacological effects. These include increasing heart rate (pulse increase), stimulating the central nervous system, increasing the contractile force of the heart, and stimulating intestinal peristalsis. Caffeine also has a weak diuretic effect and may inhibit muscle contractions in the walls of the female fallopian tubes, possibly impeding the passage of fertilized eggs into the uterus. According to a new study, it is also able to improve long-term memory and increase the speed of thought processes.
Caffeine in cosmetic products
And caffeine has also been able to prove its extraordinary mode of action in cosmetics. In skin care products, caffeine is usually used in the form of an extract or as a component of a cream or serum. It is often combined with other ingredients such as antioxidants, moisturizers, and skin-conditioning compounds to provide additional benefits to the skin.
For example, the substance is used quite specifically in hair care products to combat hair loss. The caffeine penetrates deep into the hair roots and stimulates or activates them. The effect has been established beyond doubt by the Friedrich Schiller University in Jena. However, this only works if the products are used correctly. Shampoos with caffeine in particular must be allowed to act for a certain time in the hair so that the active ingredient is optimally transported to the hair roots. Caffeine remains in the scalp for around 24 hours, after which it is broken down. The hair roots are then no longer sufficiently supplied with caffeine, so regular application is essential if a growth-promoting effect is desired.
The substance is a true all-rounder in the beauty sector. In eye creams, the substance has a decongestant effect, and it has also been proven to have a firming effect on the skin, so it is used in numerous high-quality massage creams and massage oils. In addition, caffeine is used in many care products against cellulite. The reason: the substance dehydrates the tissue on the one hand and at the same time activates an enzyme that helps to split and break down fat. Effective in this context are not only creams, but also coffee peelings. These are sometimes even used as home remedies: In this case, two to three tablespoons of coffee powder must be mixed with the same amount of body oil and then applied to the desired areas. Before rinsing off, this mixture should be allowed to soak in for a few minutes.
Nonetheless, the substance is additionally capable of slowing down the skin aging process. The substance circulates and tightens the skin, as it ensures that the skin cells are stimulated to renew themselves faster. As a result, the skin can absorb other nutrients and active ingredients much better. Finally, caffeine even has an anti-inflammatory effect: in the form of facial toners, the substance causes pimples and inflammations to heal better.
If you would like to have your own cosmetics produced with caffeine, you have come to the right place.
PROFILE
INCI name: Caffeine
Alternative names: 1,3,7-trimethylxanthine, methyltheobromine, tein, theine, guaranine
Function: skin caring
CAS number: 58-08-2
EINECS/EILINCS-Nummer: 200-362-1
Properties: bitter tasting crystals, colorless and odorless
Solubility: good in chloroform, moderate in water and alcohol
The all-rounder in the beauty sector
Caffeine not only has a stimulating effect on body and mind, but also fulfills important tasks in cosmetics. Whether in the fight against the dreaded hair loss, for cellulite or simply to improve the appearance of the skin: it is a true all-purpose weapon and is free of serious side effects when used externally. US scientists have even recently confirmed that regular moderate consumption of coffee can prevent skin cancer. How this protective mechanism works in detail, however, has not yet been clarified. What is certain, however, is that caffeine in cosmetic products has a variety of effective modes of action.
Sources:
Evaluation of caffeine as inhibitor against collagenase, elastase and tyrosinase using in silico and in vitro approach.; J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2019 Dec;34(1):927-936.
Caffeine and Its Pharmacological Benefits in the Management of Androgenetic Alopecia: A Review.; Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2020;33(3):93-109
Caffeine Protects Skin from Oxidative Stress-Induced Senescence through the Activation of Autophagy.; Theranostics. 2018 Nov 10;8(20):5713-5730.
A Review of the Role of Green Tea (Camellia sinensis) in Antiphotoaging, Stress Resistance, Neuroprotection, and Autophagy.; Nutrients. 2019 Feb 23;11(2):474.
Development, Characterization, and Stability Evaluation of the Anti-Cellulite Emgel Containing Herbal Extracts and Essential Oils.; Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Aug 25;14(9):842.