Solubilisers
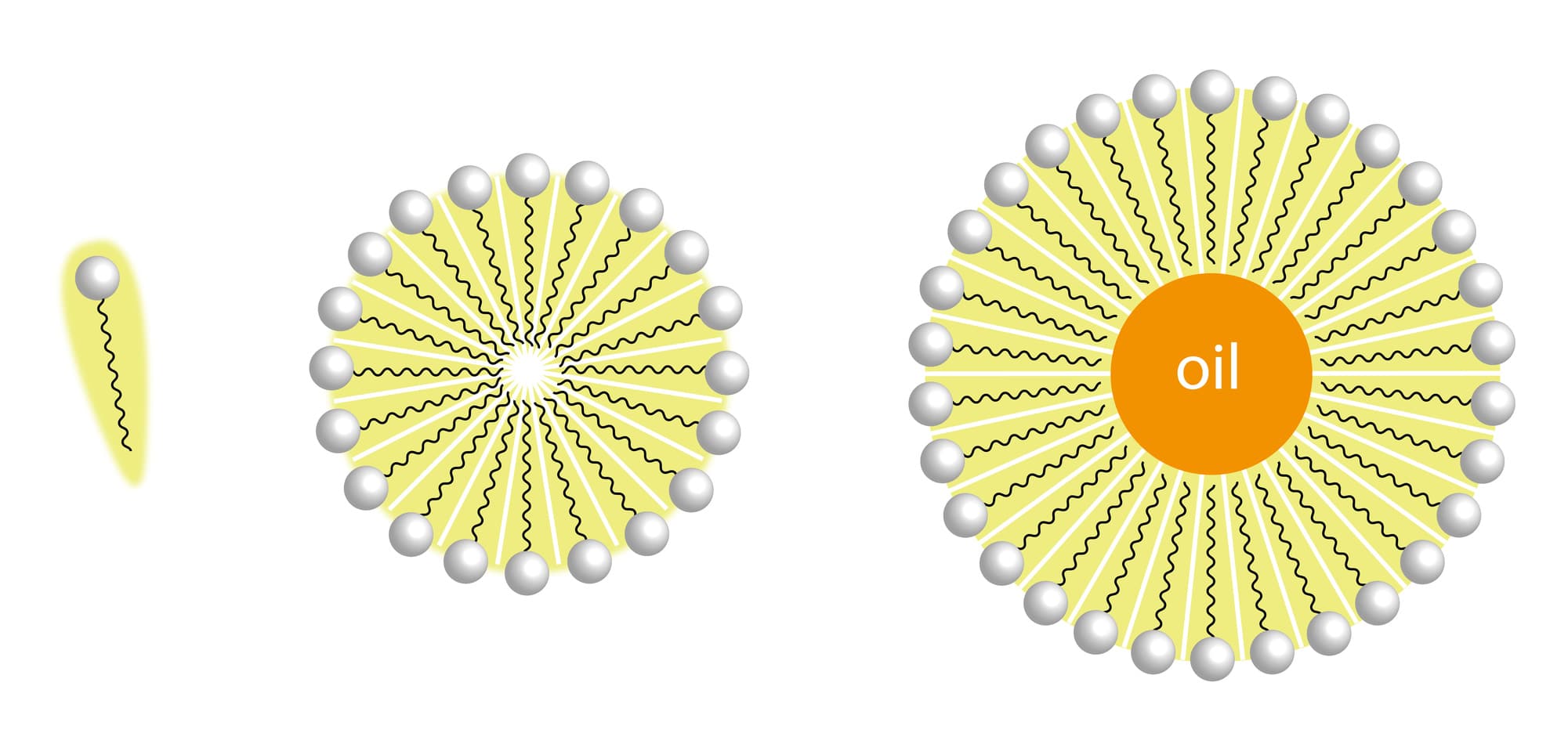
What are solubilisers?
Solubilisers are amphiphilic compounds that spontaneously form micelles in water or aqueous solutions. Solubilisers are used in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals to ideally convert poorly soluble substances, perfume oils or lipids into clear solutions.
Solubilisation is an improvement in solubility using solubilisers that are able to convert poorly water-soluble or even water-insoluble substances into clear, at most opalescent aqueous solutions without changing the chemical structure of these substances.
The solubilisates produced are such that the slightly water-soluble or water-insoluble substance is dissolved in the molecular associates of the solubilisers that form in aqueous solution – the so-called micelles. These solutions are stable single-phase systems that appear optically clear to opalescent and can be produced with practically no energy input.
Innovative application of this class of raw materials
Micellar water is an attractive application for solubilisers. Such products can be used as a toner, make-up remover and cleanser in one.
Filled in a pump foamer as a packaging material, a micellar water even becomes a cleansing mousse. Micellar water is an innovative product that replaces your typical cleansing routine in a single step. Micellar waters are so gentle on the skin and still remove all traces of dirt and make-up. However, waterproof make-up often needs to be removed 2-3 times because micellar water only contains very mild cleansing surfactants. Micellar water with very mild solubilisers is also ideal for use as an eye cleanser.
What else are solubilisers used for?
Solubilisers are mostly used to improve the appearance of cosmetic formulations by making the formulations transparent. In addition, the bioavailability and thus the effect of active ingredients can be increased by using solubilisers. In this way, active ingredients can be used more efficiently and preservatives, for example, can also be reduced. Many solubilisers act as so-called boosters.
The classic solubilisers for cosmetic active ingredients and perfumes are
- ethoxylated (hydrogenated) castor oil (e.g. Cremophor RH 40, PEG-40 Hydrogenated Castor Oil)
- ethoxylated sorbitan fatty acid esters (e.g., Tween 20, Polysorbate-20)
These classics are increasingly being replaced by PEG-free solubilisers in modern cosmetics.
We formulate exclusively with the following solubilisers:
| Tradename | INCI | Supplier | Remarks | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eumulgin HRE 40 | PEG-40 Hydrogenated Castor Oil | BASF | Classic | |
| Eumulgin SML 20 | Polysorbate-20 | BASF | Classic | |
| Eumulgin HPS | Coceth-7 (and) PPG-1 PEG-9 Lauryl Glycol Ether (and) PEG-40 Hydrogenated Castor | BASF | PEG | |
| Eumulgin L | PPG-1 PEG-9 Lauryl Glycol Ether | BASF | PEG | |
| symbio solv clear | Caprylyl/Capryl Glycosides (and) Aqua (and) Sodium Cocoyl Glutamate (and) Polyglyceryl-5 Oleate (and) Glyceryl Caprylate (and) Citric Acid | Evonik/Dr. Straetmans | PEG-free | |
| Tego Solve PC 61 | Polyglyceryl-6 Caprylate (and) Polyglyceryl-4 Caprylate (and) Polyglyceryl-4 Cocoate (and) Polyglyceryl-6 Ricinoleate | Evonik | PEG-free | |
| Radia 7931 | Polyglyceryl-4 Caprate | Oleon | PEG-free | |
| dermofeel GW10L | Polyglyceryl-10-Laurate (and) Aqua (and) Citric Acid | Evonik/Dr. Straetmans | PEG-free | |
| Sepiclear G7 | Heptyl Glucoside | Seppic | PEG-free | 1 part raw material to be solved: 5 parts solubilizer |
| Natisol | Cocoyl Proline | Sinerga | PEG-free | 1 part raw material to be solved : 10 parts solubilizer |
| Tego Solve 55 | Polyglyceryl-3 Caprylate/Caprate/Succinate and Propylene Glycol | Evonik | PEG-free |
Literature:
A Method of Solubilizing and Concentrating Astaxanthin and Other Carotenoids. Hara KY, Yagi S, Hirono-Hara Y, Kikukawa H.Mar Drugs. 2021 Aug 16;19(8):462.
Cyclodextrins for the Delivery of Bioactive Compounds from Natural Sources: Medicinal, Food and Cosmetics Applications Christaki S, Spanidi E, Panagiotidou E, Athanasopoulou S, Kyriakoudi A, Mourtzinos I, Gardikis K.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Sep 8;16(9):1274.
Microemulsions and Nanoemulsions in Skin Drug Delivery. Souto EB, Cano A, Martins-Gomes C, Coutinho TE, Zielińska A, Silva AM.Bioengineering (Basel). 2022 Apr 5;9(4):158.