Collagen
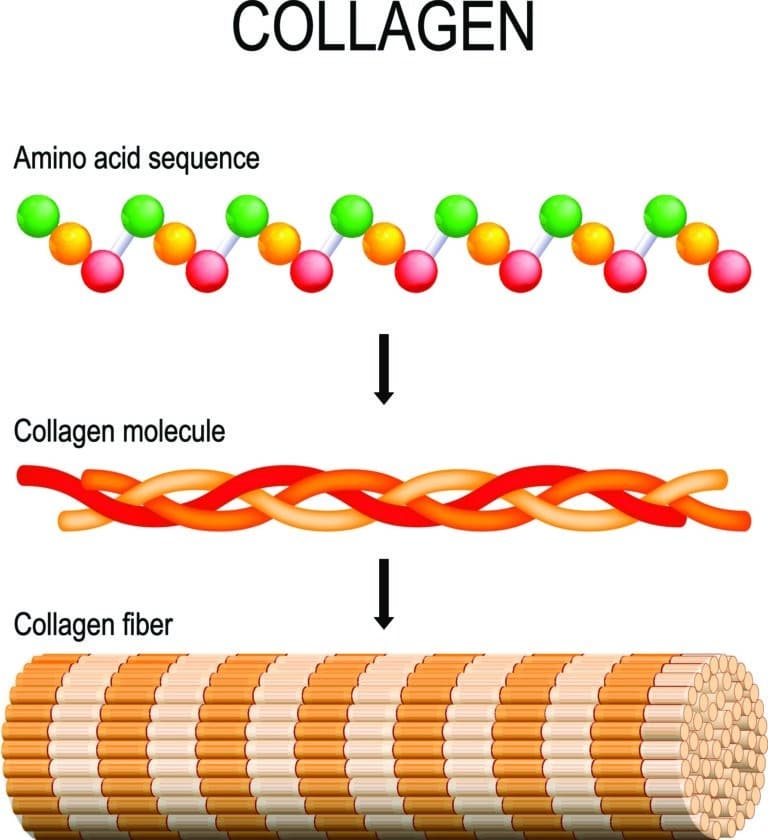
The essential precondition for skin that is wrinkle-free and elastic as long as possible is the perfect structure of collagen. The substance is the pivotal fiber material of our bones, cartilage, tendons, blood vessels, teeth and the skin.
What is the secret of collagen? Which are the components of this miracle material? What are its functions in the organism? What is its role in cosmetics?
Collagen is the predominant protein in the human body with a percentage of 30 percent of all proteins in the organism. It amounts to nearly six percent of the total body weight; that means 3.6 kilograms for a person of 60 kilograms. Being a so-called structural protein, collagen provides firmness for many body parts. For example, it maintains the tensile force of the connective tissue and the tightness of the body silhouette. The strong collagen structure is the basis of the fitness of the bones, healthy hairs and smooth skin. It is essential for the tear and pressure resistance of the pulmonary tissue, the tendons and ligaments and the blood vessels. The mechanical resilience of collagen fibers is nearly ten thousand times as high as their own weight. The non-elastic fibers consist of over 1000 amino acids. Collagen is built by the fibroblasts which are cells of the connective tissue. The amino acids are stringed together by the fibroblasts to form alpha-chains (polypeptides) and the predominant amino acids are glycine, hydroxyproline and proline. The percentages within the collagen structure: glycine 33.0 percent, proline 12.0 percent and hydroxyproline 10.0 percent.
According to the current state of science, there are 28 different collagen types numbered consecutively from type I to XXVIII.
- Type I is the predominant collagen in humans and other mammals. It is mainly responsible for skin, bones, tendons, dentine, fascia, inner organs and vessels.
- Type II fulfills important tasks in the cartilage and the vitreous body of the eye.
- Type III is fundamental for the firmness of skin, uterus and blood vessels.
For the sufficient production of collagen, the body requires not only amino acids but also vitamin C. It is an essential cofactor of the collagen-building enzymes. A well-known example is the scorbutic disease that struck many sailors in former times. The sailors lost their hair and teeth during long sea travels. The dreadful scurvy was caused by a severe lack of vitamin C resulting in a dramatic reduction of the production of collagen fibers. A balanced diet should contain not only sufficient amounts of food rich in amino acids (fish, meat, bone bouillon, egg) but also food rich in vitamin C to support collagen production in the best way.
Breakdown of collagen and how to boost its production
The collagen reservoir is corroded by unfavorable life habits and environmental stressors. Smoking, stress, excessive sun exposure or chronic illness result in decreasing collagen production. With age bones lose stability, hair becomes thinner, tendons lose flexibility and skin slackens. Menopause and dropping estrogen levels add to receding collagen synthesis and aggravate wrinkles and states of dry skin.
Fortunately, collagen-containing cosmetics offer useful solutions.
However, the production of collagen is not really uncomplicated. It is produced only by human beings and animals and currently not available in a purely vegan or plant-based version. Animal collagen primarily is obtained from pigs or cows. Other sources are chickens, caviar or fish skin. However, meanwhile alternatives for vegetarians, vegans and/or allergy sufferers have been discovered. Such an alternative is collagen from jellyfish. Jellyfishes have no nervous system and are said to be “insensitive to pain”. Jellyfish collagen therefore is considered to be an acceptable solution for natural cosmetics.
A substance similar to collagen is “collageneer”. It is derived from the seed skin of the white lupin. It is able to increase skin’s collagen production and its use in natural cosmetics is of growing interest.
There are many plants providing amino acids and vitamin C valuable for collagen synthesis.
Also, a well-balanced diet can boost collagen production. Food rich in glycine and proline such as seeds of sesame, poppy, hemp, sunflowers or yeast flakes and peanuts is ideal to combine with food rich vitamin C like sea buckthorn, rose-hip, guava and acerola.
The effects of collagen-containing cosmetics on skin
Plump skin does not only require sufficient water but also the perfect synthesis of collagen. Ideally the substance builds a structure supporting skin and its optimal tonicity. With age, skin loses elasticity and firmness. Moreover, decreasing estrogen levels cause collagen production to reduce and consequently weaken the collagen structure.
Where in the skin are the collagen fibers?
The skin is composed of three layers: the upper layer called epidermis, the middle layer called corium or dermis, and the deepest layer called subcutis. The collagen is the key component of the connective tissue, that is the middle skin layer, the dermis.
Skin-firming collagen can be supplied externally by excellent cosmetics and be an alternative to botox, surgical lifting or wrinkle treatment by injections of body-own fat. Anti-aging creams mainly with bovine collagen have been used already for several years. Today also collagen-containing serums, hydrogels, hand creams, facial masks or eye masks and eye pads are available. The products can be recognized by such ingredients as collagen hydrolysate or collagen peptide.
Collagen hydrolysate is derived from collagen; however, it differs from gelatin in so far as is slightly enzymatically modified and therefore easily water-soluble. Collagen peptide is only another term for collagen hydrolysate. The collagen component covers skin’s surface with a water-binding film giving the complexion a plumper and younger appearance. Used as a direct cosmetic ingredient it has good hydrating properties. It protects skin from drying out and softens the complexion. However, generally the collagen molecules are too large to penetrate into skin. Their field of action is skin’s surface. They cannot penetrate the upper skin layer (epidermis) and therefore will not reach the dermis. That means they do not directly influence the connective tissue. Used in anti-cellulite products, the protein improves skins outer appearance and leaves the problem zones looking firmer.
The external application of the ingredient cannot wipe away lines and wrinkles. Combined with skin-similar moisturizers and antioxidants (e.g. vitamin C and retinol), it will leave skin looking clearly smoother, firmer and supple.
There is good reason to be optimistic. Scientists are working on enzymes able to micronize the macromolecules. The substance could be carried into deeper skin layers using hyaluronic acid as a vehicle. It will take some time before this technology is ready for use.
Collagen has also many benefits for the hair. As an ingredient in high-quality hair care products it smooths hair and makes it easier to comb. Collagen promotes a “fuller” look, an effect that is increasingly used for mascaras and lip care products.
Collagen can be used as a food supplement and work within the body. The content of the ampoules or the pulverized substances are taken in orally to be carried by the blood circulation to their site of action: the dermis, i.e. the middle skin layer.
Another mode of application is the injection of collagen into the skin. Skin is plumped up, reducing the depth of wrinkles and smoothing them. However, the injections have two considerable disadvantages. They are rather expensive and they have to be repeated regularly because the body degrades the collagen in the course of time. In addition, the risk of allergic reactions is rather high.
The good quality of collagen is essential
Collagen in its pure form is an animal product (with exception of the alternatives mentioned before). Therefore, it ideally should be derived from animals kept and fed in accordance with the current bio standard. Grazing and free-range practices are ideal for cattle, pigs and chickens. It is important that the collagen is processed carefully to develop its full potential in the finished product. It should be free of additives or filling stuff (e.g. sugar). The combination with hyaluronic acid and vitamin C is favorable for the effects on the collagen synthesis. Collagen intended for the use in cosmetics frequently is prepared from cooking gelatin. In that case best quality is important as well.
Cosmetics with collagen in rare cases can cause allergies. The higher the affinity of the animal-derived substance with the human organism, the lower is the risk of allergy. Chickens, cows or pigs are better suited sources than jellyfishes.
Portrait Collagen
INCI: Collagen
CAS number: 9007-34-5
EINECS number: 232-697-4
Effects: increases skin’s water content, makes hair supple and easier to comb
INCI: Hydrolyzed Collagen
CAS number: 92113-31-0
EINECS number: 295-635-5
Production: by acid, alkaline or enzymatic hydrolysis from collagen
Effects: as mentioned above
INCI: Soluble Collagen
EINECS No.: 232-697-4
CAS No.: 9007-34-5
Soluble collagen comes typically from fish skin. Soluble collagen has undamaged, i.e. skin identical, structure. Through special physico-technical process steps it has a minimized odour.
What is soluble collagen?
Soluble collagen is a form of collagen that is soluble in water or other liquids. Collagen is normally a solid fibre that is difficult to dissolve in water, but through special processing it can be broken down into smaller, soluble fragments.
Soluble collagen is often used in cosmetic products because of its ability to absorb and retain moisture. It is often used as a moisturising ingredient in creams, lotions, serums and other skin care products to hydrate, soothe and smooth the skin.
There is also evidence that soluble collagen may play a role in improving the elasticity and firmness of the skin. When applied to the skin, it can help strengthen the skin’s moisture barrier and promote collagen production.
It is important to note that soluble collagen is not the same as endogenous collagen and is not able to perform the same structural functions as endogenous collagen. However, it can be useful as a skin nourishing ingredient, helping to increase skin hydration and reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
What are the options for avoiding animal collagen in cosmetics?
There are several ways to avoid animal collagen in cosmetics. Here are some examples:
- Plant collagen: As mentioned above, there are companies like Geltor that produce collagen from plants. This type of collagen is suitable for vegetarians and vegans and contains no animal ingredients.
- Peptides: Peptides are short chains of amino acids that can provide similar benefits to collagen. These can be derived synthetically or from plant sources and can be used in cosmetics to increase skin hydration, improve elasticity and reduce fine lines and wrinkles.
- Collagen stimulants: There are ingredients that can stimulate the production of the body’s own collagen, such as retinol, peptides and growth factors. These ingredients can help improve skin elasticity and firmness.
One of these novel peptides is Geltor’s HumaColl21.
HumaColl21 is a collagen product manufactured by Geltor. Collagen is an important structural protein found in many tissues of the body, such as skin, bone, cartilage and tendons. It is also an important ingredient in cosmetics and dietary supplements.
Geltor has developed a unique method to produce plant-based collagen by using the genetic material of plants to produce collagen proteins. This plant-based collagen has the advantage of being free of animal ingredients, making it suitable for vegetarians and vegans. It is also free from allergens that can be found in animal collagen.
HumaColl21 is used as an ingredient in cosmetics and skincare products to increase skin hydration, improve skin elasticity and reduce fine lines and wrinkles. It is also used in dietary supplements to support skin health and promote bone growth.
Superior cosmetics with collagen by Cosmacon
While collagen is not a miracle cure, in cosmetic products the valuable protein can be instrumental in making skin look smoother, softer and plumper. Whether serum, cream or mask
Collagens are ideal for having your cosmetics made. Together with Cosmacon, you develop your product, so that this is sure to be the successful start to building your own brand.