Ectoine
Most cosmetic active ingredients have been known for a very long time. Just think of frankincense, myrrh, gingko or camomile. Some of them were already used in ancient times and are still used in many products today thanks to their good properties. The situation is quite different with ectoine. This natural substance, which belongs to the extremolytes, was only discovered for the first time in 1985. Scientists discovered it in the purple bacterium Halorhodospira halochloris.
This bacterium in turn originated from a salt lake in the Sketic Desert (Wadi El Natrun / Egypt), which was actually considered “dead” and completely hostile to life. It is now known that ectoine occurs in precisely such extreme environments in numerous halophilic, gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria: not only in deserts, but also in geysers and even in the ice of the Arctic.
The substance is a cyclic amino acid that is sometimes called a stress molecule due to its extraordinary properties. Its high medical, biochemical and cosmetic benefits are impressive.
What exactly is ectoine?
In reference to the extreme environmental conditions, naturally occurring, low-molecular substances such as ectoine are called extremolytes. The name could not be more appropriate.
A brief explanation: To enable microorganisms to survive even under extreme conditions in places where no form of life would actually be possible, they form ectoine in the cytoplasm. This substance protects the bacteria from even the most extreme environmental factors and thus ensures their existence. It regulates osmotic stress, has a hydrating effect and protects or stabilizes enzymes, proteins, cell membranes and nucleic acids, but without directly interfering with the metabolism of the microorganisms.
This is the only way for bacteria to survive despite adverse external conditions. High salt concentrations, drought, strong temperature fluctuations and extreme solar radiation can then no longer harm them. This is a clever natural strategy that has been tried and tested for millions of years and has also been used in cosmetics since 2001. Incidentally, the bacteria love the extreme conditions and have adapted perfectly to them. They would not survive in a “normal” environment by our standards!
Many studies have been carried out on the substance since its discovery in 1985. It is now known that ectoine as a medicinal product can help with inflammatory skin and mucous membrane diseases. Common indications include colds, respiratory diseases, allergies, psoriasis, neurodermatitis and eczema. The active ingredient can be found in nasal, mouth and throat sprays, inhalation solutions, eye drops and creams. For example, inhaling a saline solution containing ectoine is said to protect and moisturize the airways.
No persistent or repeated side effects have been observed to date, as the physical mechanism of action does not interfere with processes in the human body.
In a few individual cases, a temporary, slight and localized burning sensation has been experienced after application to the skin.
If you already know that you are hypersensitive to ectoine, you should not use such products as a precaution. There is currently no data available on use during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
In biochemistry, the substance is used to stabilize proteins, nucleic acids and other biologically active substances.
Ectoine in cosmetics
Ectoine stabilizes and maintains the functionality of various biological structures.
The substance influences water molecules by strengthening the interactions between them. As a result, the molecules form a structure that resembles a close-meshed and dense net. Ectoine then forms a stable layer of water around itself and the surrounding proteins or cell membranes. In other words, the active ingredient surrounds the skin with a protective coating of tiny water molecules.
Thanks to this layer, ectoine provides very effective protection against external stress factors, so much so that the process has been given its own name. Scientists refer to the effect as “Ectoine Hydro Complex”. In the treated regions, the water layer repels pollutants from the environment and allergens (e.g. fine dust). As a protective barrier, it can also prevent factors such as sunlight, heat, cold or salt water from causing damage. The moisture content of the skin is increased, which in turn counteracts dehydration. Products with Ectoine can therefore reduce wrinkles, make the skin appear firmer and smoother and support regeneration.
They are also able to protect against premature, environmentally-induced skin ageing and the negative effects of harmful UV radiation. Irritated skin is soothed and any inflammation is inhibited. Its effectiveness has already been proven by extensive studies.
Anyone wishing to launch highly effective cosmetics with Ectoine on the market can therefore draw attention to their products with a wide variety of claims.
Some examples:
– Reduces lines and wrinkles
– Strengthens and repairs the skin barrier
– Protects the skin from environmental skin ageing and stress factors
– Soothes inflamed and irritated skin
– Prevents UV-induced damage to the skin
– Reduces skin redness
– Reduces transepidermal water loss from the skin
– Smoothes flaky and/or rough skin
– Increases long-term skin hydration
– Protects and strengthens the skin’s defense system
The extraction of ectoine
Of course, the substance is not obtained directly from the desert or the Arctic, as this would not be sustainable. Science is now able to produce the active ingredient using a complex process known as “bacterial milking”. This process also has the advantage that ectoine is not produced artificially, but is extracted from bacteria. For this purpose, extreme conditions are simulated, which usually means that the bacteria come into contact with a high concentration of salt, causing large quantities of the protective ectoine to form. By subsequently rinsing the bacteria with a salt-free solution, the stored ectoine can be released and extracted.
Ectoine profile
INCI: Ectoin
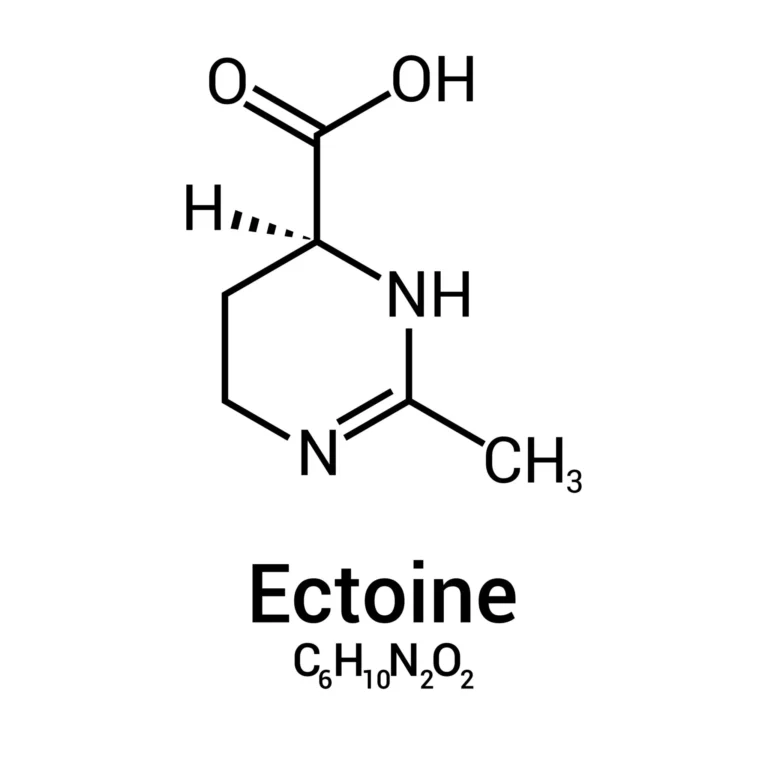
Alternative name: (S)-2-methyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydropyrimidine-4-carboxylic acid
Definition: a natural substance belonging to the extremolytes, which is formed by salt-loving bacteria under extreme environmental conditions
CAS number: 96702-03-3
Molecular formula: C6H10N2O2
Description: a colorless to white powder
Solubility: good in water
Melting point: 280 degrees Celsius (decomposition)
Effect: protects against external stress factors, nourishing, stabilizes the skin barrier, anti-inflammatory
Possible applications: as anti-ageing care and for stressed, irritated, damaged and irritated skin
Recommended application concentration: 0.3 – 2.0 percent
The all-rounder is a miracle of nature
Ectoine is a natural, multifunctional and highly effective substance that has been proven to prevent skin and cell damage and promote skin repair and regeneration. It is not only suitable for mature skin, but also for damaged, sensitive, irritated and atopic skin. Let your target group benefit from this self-defense strategy of nature and add high-quality products with Ectoine to your skin care line! Cosmacon will be happy to help you with the development and implementation.
Literature:
Czech L, Hermann L, Stöveken N, Richter AA, Höppner A, Smits SHJ, Heider J, Bremer E.Genes (Basel). 2018 Mar 22;9(4):177
Juncan AM, Morgovan C, Rus LL, Loghin F.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Oct 18;15(20):4134.
Ectoine disperses keratin and alters hydration kinetics in stratum corneum.
Bow JR, Sonoki Y, Uchiyama M, Dauskardt RH.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2021 Sep 17;28:101134