N-Acetylneuraminic acid
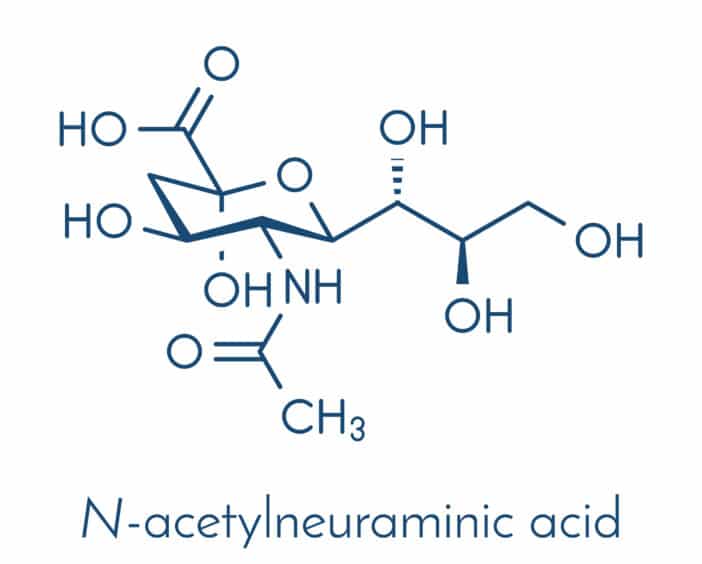
N-Acetylneuraminic acids are the N- and O-derivatives of acetylneuraminic acid. As a rule, the term N-Acetylneuraminic acid refers to N-acetylneuraminic acid, which also occurs in the human body. As a component of amino sugars, N-acetylneuraminic acid assumes an important protective function and protects proteins from being cleaved by peptidases or proteases. However, there are other neuraminic acid derivatives, such as N-glycolylneuraminic acid, which occurs in mice. This article is about N-acetylneuraminic acid, which is abbreviated NANA, SA or Neu5Ac.
In human tissue, this substance is found almost everywhere, but mainly in body fluids, glandular secretions, and blood plasma. It can be found in saliva and cerebrospinal fluid as well as in urine, breast milk (especially colostrum with a content of 880 to 1780 milligrams per litre!) and amniotic fluid. In addition, larger concentrations can be detected in the kidneys and in the brain.
N-Acetylneuraminic acid has a great influence on mental development. In the bodies of pregnant and breastfeeding women, the concentration of sialic acid is particularly high so that babies are adequately supplied during the immensely important stage of brain development (from pregnancy to the second year of life). In addition, N-Acetylneuraminic acid plays an important role in the development of the immune system. For these reasons, it is also found in baby food. This ensures that babies are supplied with the important substance even if the mother does not breastfeed her child.
Also interesting for cosmetic use
Sialic acid is used, among other things, in the production of medicines: for example, against influenza or against Alzheimer’s disease. The substance can also be used very well in cosmetic formulations. Cosmetic manufacturers in South Korea, Japan and other Asian countries launched the first creams, face masks, essences and sprays containing N-Acetylneuraminic acid on the market some time ago.
There, they are often produced according to a traditional Chinese “recipe” and contain natural saliva extract from the nests of swallows, which has a particularly high N-Acetylneuraminic acid content.
Corresponding products are actually very successful, as they are considered to be extremely effective, especially in the field of anti-ageing.
N-Acetylneuraminic acid prolongs the life of human skin cells and is an effective MMP-1 inhibitor. It is able to restore already senescent skin cells to their original state and can maintain cell stability. In addition, it is said to have a lightening effect (“bleaching”) as it suppresses the production of melanin by inhibiting the bioactive expression of dopahydroxylase as well as tyrosine hydroxylase. This makes it the perfect active ingredient for first-class cosmetics in the premium segment. It is recommended for a wide variety of anti-aging products, but especially for creams and serums.
Fact Sheet N-Acetylneuraminic acid:
INCI: Salic Acid
CAS no.: 131-48-6
EINECS No.: 205-023-1
Description: White powder
Effect: N-Acetylneuraminic acid has a great influence on the development of the brain and plays an important role in cell contacts. By binding bacteria and viruses, it is involved in immune defence, among other things. Used cosmetically, it has a brightening effect and prolongs the life of cells.
Fields of application: Premium anti-ageing products such as skin care creams and serums.
N-Acetylneuraminic acid in premium formulations from Cosmacon
Although N-Acetylneuraminic acid is primarily suitable for mature skin, it can also be used for the cosmetic treatment of blemished skin and/or acne due to its anti-inflammatory effect. It can lighten pigmentation or age spots and contributes to a firm, elastic, and fresh complexion by keeping the moisture molecules in the skin and thus preventing dryness. All in all, it is an equally innovative and effective ingredient for great premium cosmetic products. Cosmacon is happy to develop customised formulations for you that perfectly suit your target group.
Literature:
Lin CH, Peterson RA, Gueniche A, de Beaumais SA, Hourblin V, Breton L, Dalko M, Packer NH.Microbiol Res. 2019 Mar;220:53-6Glycan distribution and density in native skin‘s stratum corneum.
Varki, T.A.a.A., Chemical Diversity in the Sialic Acids and Related r-Keto Acids: An Evolutionary Perspective. Chem. Rev., 2002. 102: p. 439−469
Muhlenhoff, M., et al., Polysialic acid: versatile modification of NCAM, SynCAM 1 and neuropilin-2. Neurochem Res, 2013. 38(6): p. 1134-43
Schauer, R., Sialic acids as regulators of molecular and cellular interactions. CurrOpinStructBiol, 2009. 19(5): p. 507-14
N-acetylneuraminic acid keeps skin looking healthy and revitalized Cabio; by Biotech(Wuhan)Co.,Ltd